Political System
Political System
Development of the concept of the Political SystemVarious jurists have tried to explain the nature of the political system at the dawn of the 16th-17th century. Some favoured in the classical view that 'State' is an evil, which should be abolished. Others favoured the contemporary view of 'State' as the necessary institute for the regulation of behaviour. The contemporary writers are of the view that the 'State' should impose 'reasonable restrictions' in order to regulate the conduct of the people.
David Easton, Lasswell, Charles Merriam, Robert A. Dahl, Powell, Morton A. Kaplin are some of the famous political scientists contributing to the huge literature on political science.
Famous Books
Human Nature in Politics written by Graham Wallas, 1908
Arthur Bentley's book written by The Process of Government
Meaning of Political System
The term 'Political System' is related to power, rule and authority and organisation of these attributes in a systematic order.
Definitions of political system:
Robert A. Dahl:
A political system is any persistent pattern of human relationships that involves to a significant extent power, rule and authority.
Almond and Powell:
When we speak of the political system, we include all interactions which affect the use of or threat to legitimate coercion.
David Easton:
Political System is a set of interactions abstracted from the totality of social behaviour, through which authoritative values are allocated to a society.
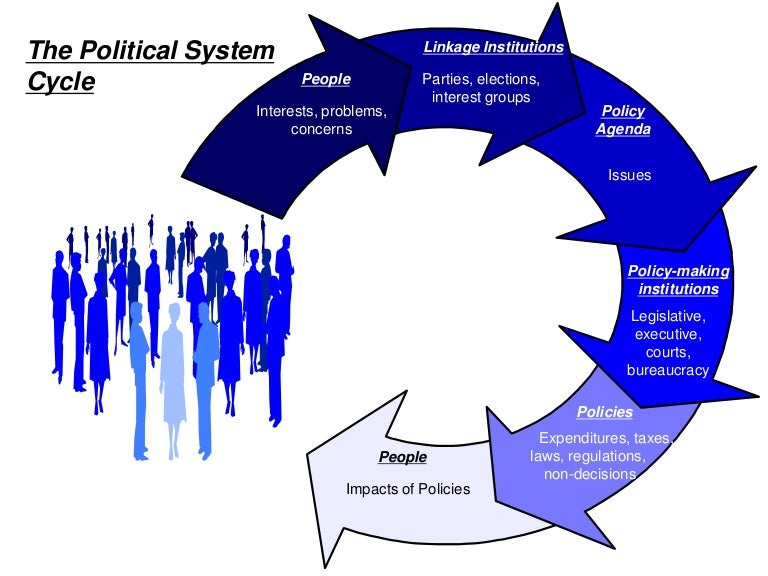
Main Characteristics of a political System
General functions of political systems:
David Easton, Lasswell, Charles Merriam, Robert A. Dahl, Powell, Morton A. Kaplin are some of the famous political scientists contributing to the huge literature on political science.
Famous Books
Human Nature in Politics written by Graham Wallas, 1908
Arthur Bentley's book written by The Process of Government
Meaning of Political System
The term 'Political System' is related to power, rule and authority and organisation of these attributes in a systematic order.
Definitions of political system:
Robert A. Dahl:
A political system is any persistent pattern of human relationships that involves to a significant extent power, rule and authority.
Almond and Powell:
When we speak of the political system, we include all interactions which affect the use of or threat to legitimate coercion.
David Easton:
Political System is a set of interactions abstracted from the totality of social behaviour, through which authoritative values are allocated to a society.
Main Characteristics of a political System
- A persistent pattern of relationships
- Comprehensiveness
- Universality
- Universality of political structure
- Universality of political functions
- Input and output functions
- Existence of boundaries
- Adaptability
- Mixed character of political system
- Multi-functionality of political systems
- Environmental impact on the political system
- Growth of the capabilities of the system
- Conversion process
- System of maintenance and adaptation of functions
Difference between the political system and the State
Nature
State: Abstract concept
Political System: Concrete in nature
Constituent elements
State: Population, People, Government, Sovereignty
Political System: Political Behaviour, political institutions, political roles
Boundaries
State: The state has territorial boundaries, it is generally permanent
Political System: Not so clear boundaries
Constitutent elements
State: Mutual human relations
Political System: Political relations and political roles
Type
State: The state has territorial boundaries, it is generally permanent
Political System: Not so clear boundaries
Constitutent elements
State: Mutual human relations
Political System: Political relations and political roles
Type
State: All States are identical
Political System: Political systems are of different kinds.
Political System: Political systems are of different kinds.
Eg: Federal or unitary, Parliamentary or Presidential system.
Interdependence
Interdependence
State: No presence of interdependence
Political System: Present in the political systems
Sovereignty
Political System: Present in the political systems
Sovereignty
State: State has sovereignty
Political System is based on power, rule and authority
Permanence
State: State is permanent
Political System: Political Authority keeps on changing (every five years)
Concept
Political System is based on power, rule and authority
Permanence
State: State is permanent
Political System: Political Authority keeps on changing (every five years)
Concept
State: Explanatory concept
Political System: Analytical concept
Organisation
Political System: Analytical concept
Organisation
State: Only formal and legal institutions
Political System: Both formal and informal organisations
Concept
Political System: Both formal and informal organisations
Concept
State: The state is an older concept
Political System: Political System is a Modern Concept
Political System: Political System is a Modern Concept
Comments
Post a Comment